Beam Test at CERN: Overview
A primary objective of the Beam Test is to validate the Monte Carlo (MC) simulations used to test the large area telescope (LAT). During the beam tests, the proton synchrotron (PS) or super proton synchrotron (SPS) will produce beam particles and dump them toward the detectors. Once analyzed, the data collected will help to better characterize the LAT's performance.
Two separate sets of detectors will be used:
- Calibration Unit (CU). Mounted on a specially constructed XY-theta table, the CU detector consists of two towers and three calorimeters. The table can be repositioned, either manually or under computer control, thereby enabling control of the angle at which the beam strikes the CU.
- Ancillary Detectors (AD). The AD detectors consist of:
- A set of plastic scintillators used for beam monitoring and trigger purposes.
- Cerinkov counters and a Transition Radiation Detector (TRD) for particle ID.
- 4 XY silicon planes and a NaI EM-CAL for tagging bremsstrahlung gammas radiated by the PS electron beam hitting the silicon planes.
The AD will be used in different configurations, depending on the setup and purpose of data taking.
Results will be analyzed using the Glast Event Analysis Machine (Gleam) and ROOT. The resulting histograms can then be compared to those obtained for comparable Monte Carlo simulations.
Monte Carlo (MC) Data
Beam Test MC data is generated in 5 steps:
- Geant4 Beam Generation – produces a ROOT-formatted file containing information about beam particles such as:
- Energy
- Trajection
- Position
- Etc.
Also produces a compiled and executable program.
- GLEAM – predicts the effect the beam will have on the detector.
For each series of particles generated in step 1, Gleam allows propagation through the calibration unit (CU), i.e., two towers and two calorimeter modules.
Produces a compiled and executable program.
- ROOT macro – takes some data from Step 1 and creates the ancillary detector data (scintillators, counters, magnet currents, etc.) that are part of the PS or SPS setup prior to the beam hitting the detector.
Produces a ROOT file for the ancillary data.
- Creates Beam Test Tuple using information from Step 2.
- Merges Merit (Step2) with Ancillary data from Step 3.
Steps: Produce(s) Comments beamtest06 Standalone package BeamtestRelease All 5 steps must be completed before Gleam can be executed BeamTest Tuple Standalone package
Also See:
- Desired Simulations (aka Revised Desired Sims List)
Beam Test Data
During approximately six weeks of testing, it is anticipated that up to 12TB of Beam Test data will be acquired and made available for analysis. Beam testing will be conducted at low energies (50MeV - 15GeV) using the Proton Synchrotron beam, and at high energies (10-300 GeV) using the Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS).
 |
 Backsplash Hitting the Left Tower |
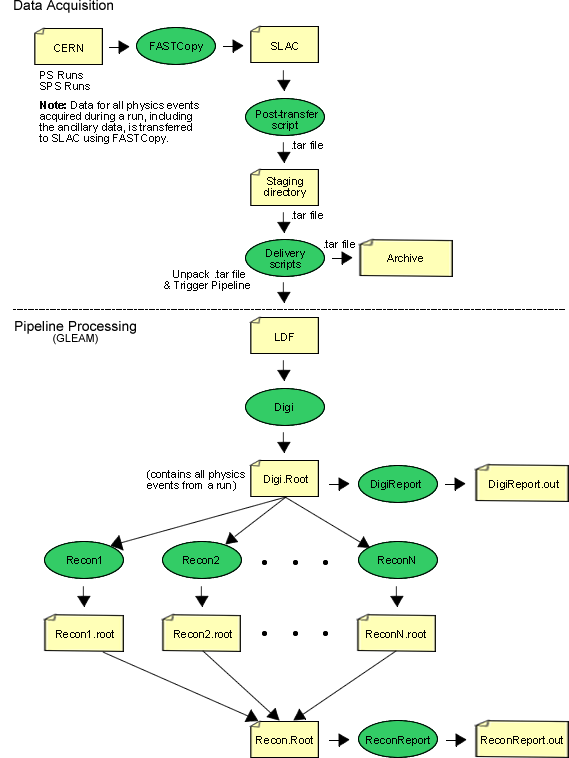
Beam Test Processing Chain
CU on XY-theta table:
The GLAST-LAT Calibration Unit (CU) consists of two towers and two calorimeters mounted on the XY-theta table which enables control of the angle at which the beam strikes the CU.

Note: Sketch shown above is from the CERN Beam Test Plan, January-2006 by Benoit Lott and Eduardo do Couto e Silva.
Proton Synchrotron Setups
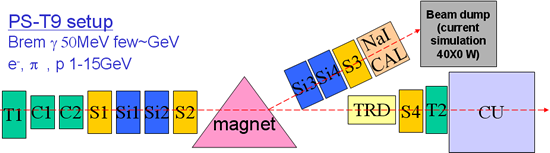
- C1-C2 Cerenkov counters (e/
PID)
- S1-S2-S3-S4 Trigger/veto scintillators
- TRD For calibration at PS; required at SPS (e/
PID):
16 modules with radiator and double straw tubes- Si-n Silicon detectors with 384 strips for
-tagger
- Nal CAL
-tagger calibration
- T1-T2 Time of Flight scintillators (protons PID)
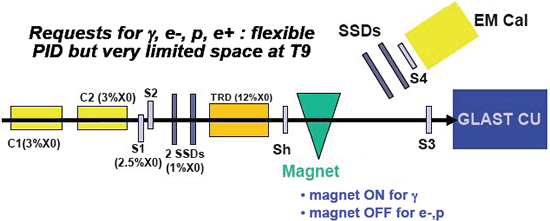
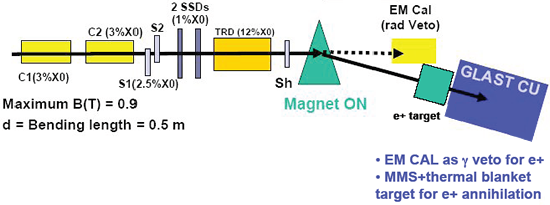
Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS) Setup
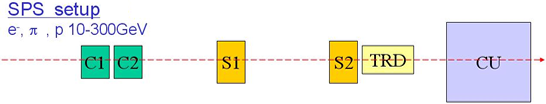
- C1-C2 Cerenkov counters (e/
PID)
- S1-S2 Trigger scintillators
- TRD For calibration at PS (e/
PID)
Also See:
Beam Test Workshop, March 2006
Status Report and Highlights from Workshop
| Last updated by: Chuck Patterson 08/01/2006 |